What Do Plants And Animals Use Nitrates For
The Nitrogen Cycle
The nitrogen cycle explains the how nitrogen flows between animals, bacteria, plants, the atmosphere, and the soil on earth. The uniqueness of the nitrogen cycle is that nitrogen is the most abundant gas in the earth's temper, almost 78% of all air, just it tin't be directly utilized past the animals and plants unless it is converted into usable compounds.
Its importance is because of its fundamental office in the formation of nucleic and amino acids. It is also an essential role of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the chief energy molecule for living things. For nitrogen to be used by plants and animals, it has to change into various states through the nitrogen wheel.
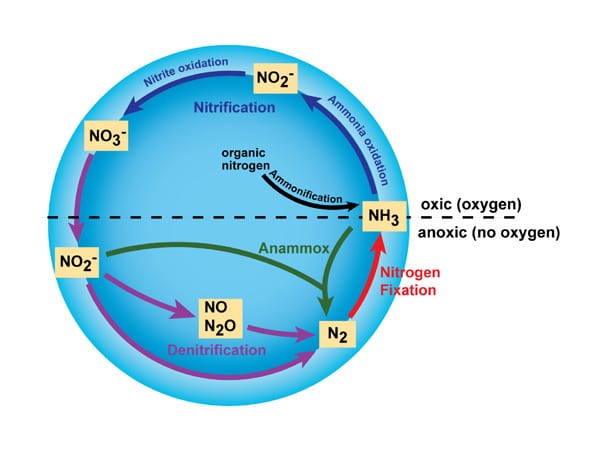
The major changes in the nitrogen wheel include nitrogen fixation, nitrification, absorption, ammonification, and denitrification. These changes to different nitrogen oxides are dependent on various activities of microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi.
Processes of the Nitrogen Bike
- Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen fixation is the procedure of converting the atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into biological state nitrogen. It is the kickoff process of making nitrogen bachelor for plants. It is defined equally an anaerobic (without oxygen) process that catalyzes the reduction of atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into ammonia (NH3).
The procedure is solely carried out by prokaryotes (bacteria) which have the natural strength to intermission the triple bond between the nitrogen atoms. These nitrogen-fixing organisms are gratis-living bacteria whereas others are symbiotic nitrogen fixers. An example of a nitrogen fixer is the Rhizobium bacteria in the roots of legumes (soybeans, peas or clovers).
Other types of nitrogen-fixing prokaryotes are extensively distributed in different environments including terrestrial and aquatic settings. A special enzyme known as dinitrogenase is responsible for the fixation process. Once the nitrogen has been reduced to ammonia, the plants can now utilise it to make other biological compounds through the synthesis of enzymes, nucleic acids, chlorophyll, and proteins.
- Nitrification
Nitrification is the process where the ammonium ions (NH4) are converted into nitrides, first into nitrites (NO2 –) then into nitrate (NO3 –). Nonetheless, this process is washed by the nitrogen-fixing bacteria. The first step is the oxidation of ammonia to nitrate, done by microbes termed as ammonia-oxidizers.
The second pace is the oxidation of nitrite (NO2 –) to nitrate (NO3 –). The participating bacteria hither are termed as nitrogen-oxidizing bacteria and they include nitrococcus, nitrobacters, and nitrosomonas.
- Assimilation
Assimilation refers to how plants and animals obtain nitrogen. Plant roots absorb nitrates from the soil into the roots and then into the entire plant system. The plants then use the nitrates in the synthesis of nucleic acids, enzymes, amino acids, proteins, and chlorophyll. On the other hand, animals assimilate nitrogen by eating the plants.
- Ammonification
Ammonification is also termed as the decaying process. Information technology occurs when the plant or animal dies then decomposers such every bit fungi and bacteria decompose the tissues and transforms the nitrogen dorsum into ammonium. The ammonium and so reenters the nitrogen cycle where it is taken up by plants and other microorganism for development. Animal waste as releases ammonium into the nitrogen cycle.
- Denitrification
Denitrification is the process that changes nitrate to nitrogen gas, hence returning information technology into the atmosphere. This procedure releases the excess nitrogen in the soil back into the temper. Special prokaryotes known every bit denitrifying leaner carry out this procedure of reversing nitrates into nitrogen gas.
Different nitrification, this process is anaerobic (uses oxygen) and the bacteria involved are in the genus Pseudomonas, Paracoccus, and Bacillus. Dinitrogen gas (N2) is the final outcome of denitrification, but other nitrogen-related gaseous forms tin too be released. A good instance is nitrous oxide (N2O) which is considered a potential greenhouse gas.
Photograph by: flickr
Source: https://eartheclipse.com/environment/process-of-nitrogen-cycle.html
Posted by: jacobssquill1950.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Do Plants And Animals Use Nitrates For"
Post a Comment